The cloud gets a lot of credit for business transformation over the last 15 years, but mobile has also been a contributing factor in changing the way we work and where we work.
watch short video > https://youtu.be/EJETHd2JZM4
According to a Microsoft study, mobile devices now account for approximately 60% of a company’s endpoints and do 80% of the work on average.
Many people prefer to check email on their smartphones, tablets have become bigger and more capable, and business mobile apps can now pretty much replicate all the functions of desktop apps in most programs.
But the problem is that while mobile use at work has increased, mobile security hasn’t kept up. A lot of companies will make sure their computers and laptops have managed security and are protected by things like antivirus and DNS filtering, but not apply those same types of protections to the mobile devices being used at the office.
One reason for this is that it’s complicated when you use a “bring your own device” (BYOD) policy for mobile device use. Companies aren’t always sure how much they can secure an employee’s personal device, yet it has access to all the same company data in most cases as that employee’s PC workstation.
How prevalent is the problem?
We’ll go through some surprising statistics in Verizon’s Mobile Security Index 2021 next, then tell you how you can improve mobile security to reduce your risk.
How Bad Is the Mobile Threat?
The Mobile Security Index 2021 report is based upon input from 13 different security companies and law enforcement agencies, along with a survey of 856 professionals focused on procuring, managing, and securing mobile devices for business.
Here are some of the findings that you need to know.
Mobile Device Breaches Can Do Major Damage
Forty percent of surveyed security professionals said that mobile devices are the biggest IT security threat that companies need to worry about, and 53% stated that their companies have experienced severe consequences due to a mobile device breach.
Some business owners are still in a mindset of thinking that since mobile devices are small, they’re only able to do a fraction of what a computer can do, thus damage is limited if they’re breached in some way.
This is not the case, with business apps leveling the playing field as to how much computing power can be done via mobile. A mobile breach or malware infection can be just as devastating as one that happens to a desktop PC.
Some of the consequences that companies suffer when a mobile device is compromised include:
- Downtime & lost productivity
- Reputation damage
- Regulatory penalties
- Loss of business
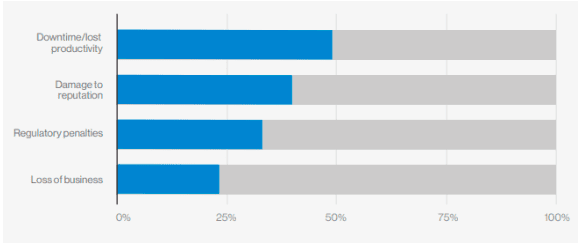
Image: Verizon Mobile Security Index 2021: Damages due to mobile compromise
Employees Often Take Fewer Precautions on Mobile Devices
Mobile devices can be more at risk because people tend not to think hackers are after their smartphones and may engage in riskier behavior on mobile than they do on their computers.
For example, here are a few findings from the Verizon report:
- 54% of companies that had a mobile breach attributed it to user behavior.
- 45% of organizations that prohibit social media use on company devices, knew employees were doing it anyway.
- There has been a 600% increase in the past year of mobile visits to adult content websites (which are often a security risk).
- 49% of employees allow friends/family to use their work devices.
Increase in Danger, Lack of Security
Mobile devices have become a growing threat to business networks largely because of two contributing factors:
- Lack of mobile security awareness among companies and employees
- Increase in attacks targeted to mobile devices
One in 25 apps was found to leak user credentials, but that’s just the tip of the iceberg when it comes to mobile security.
Some other factors contributing to mobile device vulnerability are:
- 364% increase in phishing attempts in 2020 vs 2019
- 31% of organizations relaxed their app installation restrictions during COVID-19
- 93% of Android devices are running an out-of-date OS version
- 92% of businesses don’t block the use of public Wi-Fi with mobile devices used for business
Tips for Preventing Mobile Device Compromise
Mobile devices need a cybersecurity strategy just like computers and servers. They are an increasingly vital part of the business IT ecosystem, which means a breach of one smartphone can lead to a breach of multiple computers on the same network.
Here are some protective measures you should take to secure mobile devices used for business, whether they are company-owned or employee-owned:
- Ensure all devices have mobile antivirus/anti-malware installed
- Expand your patch management program to include mobile device updates
- Use an endpoint device manager for security and control of business data access
- Include mobile device security in your employee cybersecurity awareness training
- Have employees use a business VPN when connecting to the internet on unsecured/public Wi-Fi
How Secure Are the Mobile Devices Used at Your Company?
Magnify247 can help your Hamilton County business review your mobile device security to identify liabilities and provide solutions to mitigate your risks.
Contact us today to learn more!







