Installing patches and updates for your operating system is one of the vital best practices for good cybersecurity. Approximately 60% of data breaches occur because people haven’t installed an available patch, leaving their system at risk.
watch short video > https://youtu.be/rqGvT7QkcZ8
You can get into the good habit of regularly installing patch updates for Windows by understanding the best practices of Microsoft Patch Tuesday.
Microsoft has designated the second Tuesday of every month (since way back in 2003) as the day to release security-related updates to Windows, both desktop and server, its Office software, and other related products.
Occasionally, these security patches can come on other days of the month, but you can count on seeing them on the 2nd Tuesday of every month.
Know Where to Find Updates
One best practice is knowing where to find these updates come Patch Tuesday so they can be installed on your device and any other devices that a company may have.
You’ll find all security updates issued by Microsoft, along with a summary of what it is for, on Microsoft’s Security Update Guide. This is a great place to go to become familiar with new patches and why exactly they are being released.
You will often see the Common Vulnerability and Exposure number that is associated with the exploit being patched and can search that if you like for more information.
Understanding CVE Entries
CVE entries will be short and won’t include technical data or detailed information about the potential impacts of this vulnerability or the fixes. However, they will give you a brief summary that is designed to be comprehensive and give you an idea of what this patch addresses.
Other databases where you can reference more information about the vulnerabilities being addressed in a security patch are:
The CVE IDs provide a helpful reference across all those different databases. So, knowing that is important if you want to do more research.
Understanding the Ranking/Scoring System for a Vulnerability
There is a standard for ranking how critical (dangerous) a CVE is. This standard is called the Common Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS). This is a set of open standards for assigning a number to a vulnerability to assess its severity.
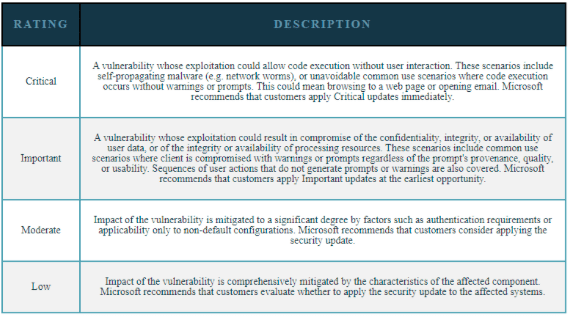
CVSS scores are listed in CVE, NVD, and CERT advisories. Scores range from 0.0 to 10.0, with higher numbers representing a higher degree of severity of the vulnerability. You can also find that security vendors have created their own scoring systems, as well. For example, below is the official rating system published by Microsoft.
Have a Process for Handling Critical Vulnerability Alerts
Every SMB needs to take notice of critical vulnerability alerts and have a process for addressing them to keep your network secure. These are often time-sensitive and need thoughtful, but quick decisions.
Having a process and guide already in place for these streamlines the process and ensures critical patches are installed right away.
Use a Cloud-based Patch Management System
It’s important to automate the patching process and not rely on manual installations, which can easily get put off. One of the best is Micro-Patching, which is designed to quickly install critical updates without interrupting users or requiring a lengthy reboot process.
Along with an automated patching process, you should also put remote monitoring and management in place for your business to ensure your systems are continually safeguarded and protected from online threats.
SMB Protections beyond Patch Management
In addition to adopting a patch management system, Magnify247 recommends the following best practices to protect individuals and businesses against, and limit damages from, cyberattacks:
- Adopt a password manager for better personal/work password hygiene: https://www.magnify247.com/password-manager-can-help/
- Require two-factor authentication on all critical accounts: https://www.magnify247.com/credential-theft-password-secure/
- Require 13+ character Passwords in your Governance Policies: https://www.magnify247.com/check-cyber-hygiene/
- Train employees to spot and avoid email-based phishing attacks: https://www.magnify247.com/incident-response-plan-part-1/
- Check that employees can spot and avoid phishing emails by testing them: https://www.magnify247.com/prevent-breaches-cyberdefend247/
- Back up data using the 3-2-1 method: https://www.magnify247.com/check-cyber-hygiene/
- Incorporate the Principle of Least Privilege: https://www.magnify247.com/cloud-jacking-keep-safe/b
- Perform a risk assessment every two to three years: https://www.magnify247.com/mckinsey-cybersecurity-predictions/
Learn More About Automating Your Patch Management
Magnify247 can help your business improve security by automating your patch management process. This frees you from worrying about any lurking vulnerabilities and ensures your network is continually protected.
Contact us today to learn more!