Modern businesses depend on digital technology to operate and thrive. This is true for all types of organizations – services, goods, storefronts, online businesses, and more. Large enterprises have the resources to maintain a dedicated in-house IT team. Smaller organizations, on the other hand, often rely on tech-savvy employees to manage the digital side of things, or they enlist outside help from an IT professional.
Regardless of whether you use the former or latter approach, small businesses, solopreneurs, and startups need to have a realistic understanding of what it takes to ensure business continuity and security in today’s tech-dense world of commerce. To help you gain that knowledge, we are rolling out a series of articles that dig into the important aspects of a secure digital infrastructure and digital business continuity.
Digital Infrastructure
Your digital infrastructure includes the computers and other devices, programs, apps, servers, internet connections, and other hardware and software upon which your business depends.
Starting with this article and over the next few posts, you’ll learn about:
-
- Specific digital security risks and how they can affect your business and customers
- Strategies to protect your business and customers from cyber threats
- Planning for digital business continuity even when the unexpected occurs
Let’s get started!
Secure your Business against Cyber Threats
In the U.S., billions of dollars are lost every year due to cyberattacks. They can target your hardware, software, business data, employee data, and customer data. Plus, cyber threat tactics are constantly evolving and becoming more sophisticated. Yikes!
Let’s look at the common delivery mechanisms cyber criminals use to launch their attacks, the damage they can do, and how to defend against them.
Threats to your Infrastructure
Businesses of all sizes and types need to protect against cyberattacks that can harm hardware and software. “Malware” is the term used for this type of threat. Malware is software intentionally designed to cause damage or otherwise interrupt the normal functioning of a digital device or network.
The two most common types of Malware threats are viruses and ransomware.
-
- A virus is malicious code designed to infect a digital device and from there spread to other connected devices. Once it gains access, the virus can damage the device and its programs, sometimes irreparably.
- Ransomware is software that infects a device and locks it down until some sort of ransom is paid, e.g., “I’ll restore access to your computer when you pay me $$.”
Viruses and ransomware are usually distributed in emails or hidden on malicious websites. Both present cleverly disguised “bait” such as a link to click or an attached file to open – hence the term “phishing.” When the user falls for the bait, it allows the malware to exploit software vulnerabilities on the device or network. Cybercriminals are very adept at making such phishing tactics appear to be from a legitimate website or organization, a person the user knows, or even from your own company.
Threats to your Data
Data theft is one of the most serious challenges facing businesses today. Cybercriminals are constantly looking for ways to steal your company and customer data, such as:
-
- Personal identity information
- Payment and financial information
- Sensitive personal or business information
Data Breaches
According to the Identity Theft Resource Center, the year 2021 set a record for data breaches in the U.S., with the most sought-after data being sensitive customer information.
Data breaches most commonly occur via spyware delivered in an email with an infected link or attachment. The spyware embeds itself in your system and steals digital information for malicious purposes: credit card theft, identity theft, industrial espionage, and others. The culprit may use the data themselves or sell it to another criminal enterprise.
Theft of these data can be catastrophic for your customers, employees, and business operations, and can seriously damage your business’ reputation.
Protect your Infrastructure and Data
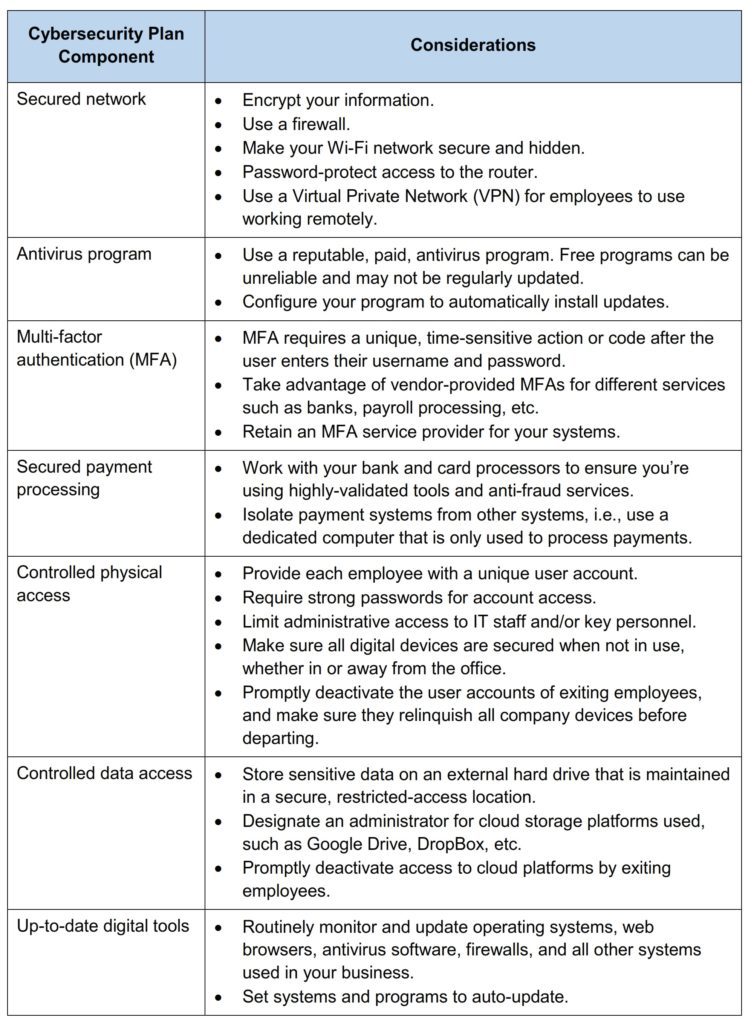
You can protect your business and your customers by establishing a cybersecurity plan and keeping it up-to-date. Below is a checklist of some of the key components of an effective cybersecurity plan.
You can download this handy checklist, with room for your notes, by clicking the image below.
This list may seem daunting, but an experienced, forward-looking IT professional can help you get your cybersecurity strategy up and running, freeing you from any angst, uncertainty, or staff limitations you may have.
Coming up next…
Our second article in this series will discuss the digital aspects of business continuity planning, including data backup, system monitoring, and preparing for unforeseeable disruptions.
We want to hear from you!
Do you have any burning questions or challenges that you’d like to hear about?
Please complete this quick, 3-question survey and we’ll get right on it!
Magnify247.com
Helping small businesses in Central Indiana maintain a secure and reliable digital infrastructure.